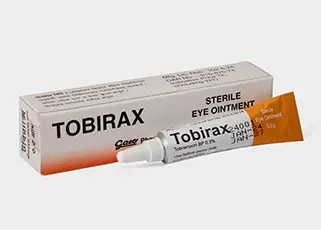
Indication:
Tobirax eye drops and ointment, a bactericidal topical antibiotic is indicated in the treatment of external bacterial conditions of the eye and it’s adnexa caused by susceptible bacteria. Appropriate monitoring of bacterial response to topical antibiotic therapy should accompany the use of Tobirax . Clinical studies have shown Tobramycin to be safe and effective for use in children.
Dosage & Administration:
Dosage and Administration: Tobirax Eye Drops: In mild to moderate disease, instill one or two drops into the affected eye(s) every four hours. In severe infections, instill two drops in to the eye(s) every hourly until improvement, following which treatment should be reduced prior to discontinuation. Tobirax Eye Ointment: In mild to moderate disease, apply a half inch ribbon into the affected eye(s) two or three times per day. In severe infections, apply a half-inch ribbon in the affected eye(s) three to four hours until improvement, following which treatment should be reduced prior to discontinuation. Tobirax eye ointment can be used in conjunction with Tobirax eye drops. Overdosage: Clinically apparent signs and symptoms of an overdose of Tobirax eye drops or ointment (punctuate keratitis, erythema, increased lacrimation, edema and lid itching) may be similar to adverse reaction effects seen in some patients. Contraindications: Tobirax eye drops and ointment are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its components Warnings: Not for injection into the eyes. Sensitivity to topically applied amino glycosides may occur in some patients, if a sensitivity reaction to Tobirax occurs, discontinue use. Precautions: As with other antibiotic preparation, prolonged use may results in overgrowth of non susceptible organisms including fungi. If super infection occurs, appropriate therapy should be initiated. Ophthalmic ointments may retard corneal wound healing. Pregnancy: Pregnancy category B. Reproduction studies in three types of animal at doses up to thirty three times the normal human systemic dose have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to Tobramycin. There are however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.